MLOps: An Introduction
Essential information about MLOps
Most of you will be very unfamiliar with MLOps. So, i’ll create this post keeping in mind that everyone is a beginner. Even if you do not understand what is machine learning, what is MLOps, or what is data science, this post will be helpful for you. The MLOps series will be a journey to understand MLOps and how it helps organizations to build, deploy, and manage machine learning models.
What is Machine Learning?
In simple words, machine learning is the process of training the machine with huge amount of data. The machine identifies the pattern and uses that pattern to make predictions or decisions. Let’s take a simple example to understand this better. Imagine you want to build a system that can predict type of a flower. You have a dataset of flowers with their features like color, shape, size, etc. You can train the machine with this dataset. The machine will identify the pattern and use that pattern to make predictions or decisions.
The Traditional Programming Problem
When you write traditional programs you need to create many if-else statements to handle every possible combination of petal and sepal measurements. This approach has serious limitations. The rules quickly become impossible to manage when you try to account for natural variations like different sized roses. When the program encounters new inputs that do not match the existing rules it simply fails to work.
The Machine Learning Solution
Machine learning takes a different approach using four key components. First you need a dataset containing large amounts of labeled flower data that includes both measurements and flower types. Second you select an algorithm based on what the specific problem requires. Third the algorithm goes through a training process where it learns patterns from the data. Fourth this training produces a model which is a mathematical function that can make predictions. The process works by having the algorithm identify patterns in the data that humans often cannot see. It creates a mathematical function that can generalize from the training examples to handle new situations. When you provide new inputs such as a petal length of 3 and a petal width of 2 along with sepal measurements the model can predict what type of flower it is.
Key Insight
The model is not the same thing as the data or the algorithm. It is the mathematical function that emerges after training is complete. How well the model makes predictions depends on two main factors. The first factor is how efficient and high quality the algorithm is. The second factor is how good and comprehensive the dataset is. This machine learning approach removes the need to write rules manually. It can handle input combinations that it has never seen before. This makes it much more robust and scalable than traditional programming methods when you need to recognize patterns.
How a model is created in realtime?
Data scientists follow eight main steps when building a model. First they gather a dataset containing information about the subject they want to study. For example a flower dataset would include measurements like petal length and width along with sepal length and width. Each entry also shows what type of flower it is. Next they divide the dataset into two sections. Typically 80 percent goes toward training while 20 percent is set aside for testing later. The third step involves picking an algorithm that fits the problem. Options include logistic regression or decision trees or k-nearest neighbors. The selection depends on what the model needs to accomplish. During the fourth step the model goes through training using the larger portion of data. The model examines the input measurements and learns how they connect to the flower types. After training comes testing. The model receives the remaining 20 percent of data to see how well it performs. This reveals whether the model can accurately predict outcomes with new information. If results are poor the data scientists return to earlier steps. They might adjust the dataset or try a different algorithm to boost performance. Once the model works well it gets saved in a format like .pkl or Joblib. This packaging allows the model to be stored and used again without rebuilding it from scratch. The final step is deployment. The model becomes part of an application or API so regular users can access it through websites or mobile apps. Following these steps helps data scientists build models that make accurate predictions.
What is MLOps?
MLOps stands for Machine Learning Operations. Think of it as DevOps but specifically designed for machine learning projects.
Learning from DevOps
The Old Way of Building Software Before DevOps existed companies struggled with slow and manual processes. Developers would write code and test it on their own computers. Then operations teams would manually set up servers and deploy everything. Every single change meant going through all these steps again. This made releasing software painfully slow. How DevOps fixed this is by introducing automation tools that handle most of this work automatically. When developers push new code, automated pipelines test it and deploy it without human intervention. Infrastructure gets managed through code instead of manual configuration. This made software delivery much faster and more reliable.
Without Automation, Machine learning teams face similar problems. Data scientists manually gather and clean data. They build models through trial and error. Engineers then manually create APIs and test everything locally. Operations teams package and deploy these models by hand. A single machine learning project might need 15 iterations of this entire process. The time adds up quickly.
How MLOps Solves This
MLOps brings automation to machine learning workflows. Automated pipelines handle data preparation and model training. When new data arrives or code changes, systems automatically retrain and deploy updated models. Infrastructure gets managed through code just like in DevOps. Monitoring tools track how well models perform in production. Companies like Netflix run both DevOps and MLOps teams. Their DevOps team manages payment systems & regular microservices. Their MLOps team handles the recommendation engine that suggests shows to watch. Both teams are essential. PayPal follows a similar pattern. DevOps engineers manage the user interface and login systems. MLOps engineers maintain fraud detection models. Each team automates their own domain.
Important Points
MLOps does not replace DevOps. Companies need both when they build traditional software and machine learning systems. DevOps automates regular software development. MLOps automates machine learning workflows. They serve different purposes but share the same goal of making teams more efficient. The main benefit is speed. Just like DevOps transformed how quickly companies could release software updates, MLOps does the same for machine learning models. Teams can experiment faster and deploy improvements more frequently. This matters because machine learning models need constant updates as new data becomes available.
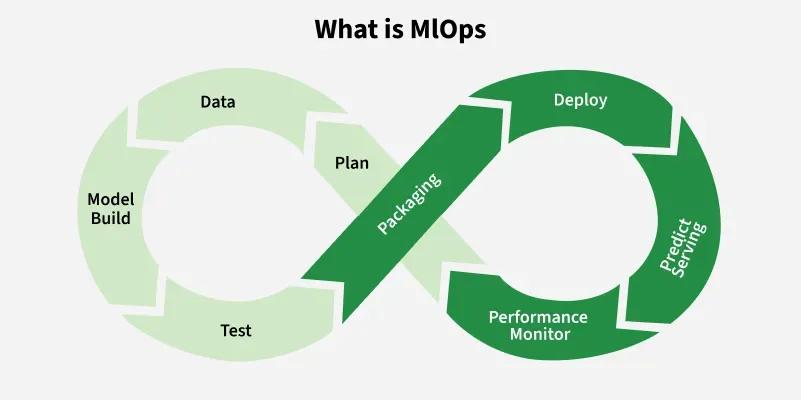
Understanding the Machine Learning Lifecycle
A machine learning lifecycle represents the full process of creating & running a machine learning model. It starts with gathering data and continues through to watching how the model performs after launch. This is not something you do once & forget about. Instead it works as an ongoing cycle of connected steps.
The Main Stages
1. Problem Definition
This stage involves understanding exactly what problem needs solving. You need to clearly state what results you want to achieve.
2. Data Collection
Here you gather information from different places. You might use datasets that anyone can access like the Iris dataset or pull information from databases and APIs and system logs.
3. Data Cleaning
This step removes duplicate entries and fixes errors in the data. Clean data leads to better model results.
4. Feature Engineering
You create new features that help the model work better. For example when predicting flower types you might add a ratio of petal length to sepal length or calculate total area. This transforms existing information into more helpful formats.
5. Model Selection
You pick which algorithm to use such as linear regression or decision trees or neural networks. The terms models & algorithms mean the same thing in machine learning.
6. Model Training
The algorithm learns from your dataset which usually means using about 80% of your data. During training the algorithm builds mathematical functions to spot patterns.
7. Model Evaluation
You test how accurate the model is using the remaining 20% of data. You decide if the performance level is good enough whether that means 90% or 95% or 99% accuracy. Sometimes you need to train again if results fall short.
8. Hyperparameter Tuning
This involves adjusting specific settings in the model to boost performance.
9. Model Deployment
You package the model into something users can access like an API or mobile app or website.
10. Model Monitoring and Maintenance
You keep checking how well the model performs over time. When accuracy drops because of new data patterns you retrain the model. Sometimes this means going back to earlier stages.
Why We Call It a Lifecycle
The process forms a circle. When a model stops performing well you might need to go back to feature engineering or try different algorithms or retrain and launch again. This pattern of constant improvement resembles how software development works.
Why This Matters for MLOps
People working in MLOps need to grasp this lifecycle because they must understand every stage involved. They look for manual tasks in each stage and then automate those tasks to make everything run smoother and more reliably. This lifecycle serves as the base for putting MLOps methods and automation into practice across the entire machine learning process.
Understanding Data Science, ML Engineering and MLOps
Data Science Role
Data scientists handle the early research and development work for machine learning projects. They start by understanding what the business needs and defining the problem that needs solving. Then they gather data from different sources and clean it up by removing duplicates & fixing errors. They create new features from the existing data and choose which algorithms & models to use. Data scientists train these models and test how well they perform. Most of their work happens in development environments on their local machines.
ML Engineering Role
ML engineers pick up where data scientists leave off. Their job is to take models from the research phase and make them ready for real-world use. They optimize models to run faster and handle more users at once. ML engineers build APIs so other systems can communicate with the models. They integrate these models into websites, mobile apps and backend systems. Their main goal is making sure end users can actually access & use the models through applications.
MLOps Engineering Role
MLOps engineers focus on automation and keeping everything running smoothly across the entire machine learning process. They build automated pipelines that can retrain models consistently. They set up continuous deployment systems so new model versions can be released safely. MLOps engineers create and manage different environments for development, testing and production using tools like Terraform. They configure systems to store and track different model versions. They set up monitoring systems with alerts to catch problems with model performance. They manage the infrastructure including Kubernetes clusters and GPU servers while keeping costs under control. They also look for manual tasks that could be automated to make the whole process more efficient.
How These Roles Differ
Data scientists build and test models. ML engineers turn those models into production systems and connect them to applications. MLOps engineers automate everything and create the infrastructure that lets the other two roles work faster and more reliably. The basic idea is that MLOps engineers create systems and processes that help data scientists and ML engineers deliver models to users quickly and safely. They do this by automating repetitive tasks, following best practices and building reliable operational systems.
I hope ML and MLOps is clear to you.
